Change Language :

Predictive maintenance: definition, benefits, examples ... all with one click!
All questions and answers regarding predictive maintenance with igus® - smart plastics

General
Advantages of predictive maintenance
Requirements for predictive maintenance
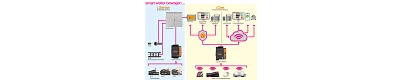
The diagram shows the importance of i.Sense as predictive maintenance sensors for i.Cee.
Application areas of predictive maintenance
Other maintenance strategies
Download more material
Consulting
I look forward to answering your questions

Shipping and consultation
In person:
Monday to Friday from 7 am - 8 pm.
Saturdays from 8 am- 12 pm.
Online:
24h
WhatsApp-Service:
Montag – Freitag: 8 – 16 Uhr





