Change Language :
Passenger boarding bridges
Without it, flying would be much less comfortable: the passenger boarding bridge (also known as the gangway or passenger boarding bridge) enables protected, level boarding of aircraft at thousands of airports worldwide. In the early days of flying, boarding was even easier. The small propeller-driven aeroplanes had small built-in steps that could simply be lowered. Even today, smaller aeroplanes generally use built-in stairs, as the gradient in the passenger boarding bridge would otherwise be too steep.
What would it look like without the passenger boarding bridge? Modern commercial aircraft have boarding heights of up to 4 metres above the ground. On giant jets such as the Airbus A380, passengers even have to board over two levels. Very high stairs would be required. And families with children, elderly and infirm passengers would find it much more difficult to board the aircraft. Not to mention protection from wind and weather.
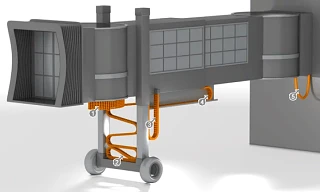
The principle of the passenger boarding bridge is simple: as a rule, one part of the system is firmly anchored to the airport building. Another part is flexibly mounted so that it can dock onto different types of aircraft. For example, differences in the height of the aircraft door as well as different aircraft lengths and widths need to be compensated for. For this purpose, a gangway usually consists of several tubes that can telescope in and out and one or more lifting units. This telescopic gangway is the most flexible variant of the passenger gangway. Less flexible designs are often only suitable for certain types of aircraft, which limits the flexibility of airport operators.
The passenger boarding bridge is moved with the help of electric motors. These require power and data cables to the control system. The movements of the individual elements are not very fast. Nevertheless, the cables must be protected from damage. As they are usually located outside the gangway, they also have to withstand wind and weather.
Advantages of igus® products in passenger boarding bridges
As aircraft idle times are becoming ever shorter and passenger boarding bridges need to work reliably, the mechanical movement must run smoothly. If a passenger boarding bridge comes to a standstill, this can mean an immediate financial loss for the airport operator, the airline and also for the passengers, who want to fly comfortably, safely and on time.
The high reliability of igus® products speaks in favour of their use in the passenger boarding bridge. The movements of the cables in the gangway can be safely guided with our e-chain systems. The strokes are mostly horizontal movements in the telescopic tunnels and vertical movements in the lifting units. The e-chain® have a long service life, so that a long service life can be expected. They can be installed in a space-saving manner so that no cables hang down and the visual appearance is not impaired. All required energy can be supplied with e-chain®, for example power and control cables, hydraulics, pneumatics, etc.
1 rotary movement e-chain systems as a reversebend radius solution 2 Lifting movement e-chain systems -
installation type " zig-zag "
3 Lifting movement e-chain systems
- installation type "suspended " 4 Horizontal movement e-chain systems - installation
type unsupported or sliding 5 Cable protection in several axes e-chain systems guide and protect in moving applications, three-dimensional
The e-chain systems reduce the required cable lengths by more than 50 % (with medium infeed) and prevent external mechanical loads on the cable, such as uncontrolled rocking, swinging, jamming etc. The low maintenance requirements reduce downtimes. The e-chain systems work ideally in conjunction with igus® chainflex® cable. Just like the e-chain®, they can withstand heat, sun, rain and snow.
Products for use in passenger boarding bridges
energy chain
Successfully in use
Consulting
I look forward to answering your questions

Lars Braun+49 2203 9649 218Write e-mail
Shipping and consultation
In person:
Monday to Friday from 7 am - 8 pm.
Saturdays from 8 am- 12 pm.
Online:
24h
WhatsApp-Service:
Montag – Freitag: 8 – 16 Uhr



